The Xsorb software is described in the following article:
Enrico Pedretti, Paolo Restuccia, M. Clelia Righi, Xsorb: a software for identifying the most stable adsorption configuration and energy of a molecule on a crystal surface, Computer Physics Communications 291, 108827 (2023), and can be downloaded from the following repository where a detailed description of the workflow and installation guide are also provided through a Wiki page.
 Molecular adsorption is the first important step of many surface-mediated chemical processes, from catalysis to lubrication. This phenomenon is controlled by physical/chemical interactions, which can be accurately described by first-principles calculations.
Several computational tools have been developed to study molecular adsorption based on high throughput/automatized approaches in recent years. However, these tools can sometimes be over-sophisticated for non-expert users.
We developed Xsorb a Python-based program for computing the adsorption energy and identifying the optimal adsorption geometry of complex molecules on crystalline surfaces.
At present, the Xsorb relies on Quantum ESPRESSO for DFT calculations. It automatically creates input files and geometries, submits the calculations, collects the data, and allows easy visualization of the results.
Despite its conceptual simplicity, this program effectively reduces the computational workload usually associated with creating and optimizing several adsorption configurations.
Xsorb workflow is schematically represented in Figure 1 on the right.
Molecular adsorption is the first important step of many surface-mediated chemical processes, from catalysis to lubrication. This phenomenon is controlled by physical/chemical interactions, which can be accurately described by first-principles calculations.
Several computational tools have been developed to study molecular adsorption based on high throughput/automatized approaches in recent years. However, these tools can sometimes be over-sophisticated for non-expert users.
We developed Xsorb a Python-based program for computing the adsorption energy and identifying the optimal adsorption geometry of complex molecules on crystalline surfaces.
At present, the Xsorb relies on Quantum ESPRESSO for DFT calculations. It automatically creates input files and geometries, submits the calculations, collects the data, and allows easy visualization of the results.
Despite its conceptual simplicity, this program effectively reduces the computational workload usually associated with creating and optimizing several adsorption configurations.
Xsorb workflow is schematically represented in Figure 1 on the right. Unit 1 is devoted the sampling of the potential energy surface (PES) that describes the molecule-surface interaction by automatically generating several adsorption configurations corresponding to different molecule-surface relative lateral positions (Figure 2) and orientations.
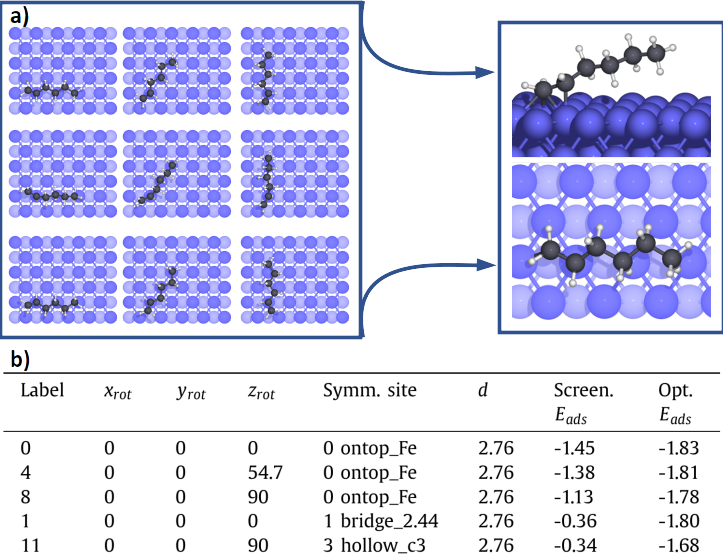
In Unit 2 The set of the most representative configurations is automatically screened through a fast pre-optimization scheme. The identified configurations are saved in a database, along with their main adsorption properties (Figure 3b): the numerical label of the configuration, rotations in degrees along x (xrot), y (yrot) and z (zrot) axis, the index and the symmetry of the adsorption site, the distance (d) between the reference atom and the surface (in Å) and the adsorption energies (Eads) of the preliminary screening and of the full optimization, in eV. The graphical representation of several configurations are shown in Figure 3a.
The most stable configuration is then identified in Unit 3 by narrowing the optimization criteria (Figure 3a).
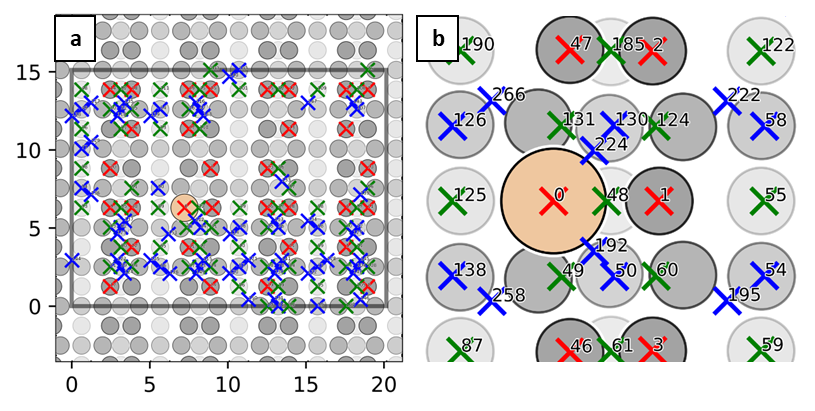
Figure 3: In panel a, visual representations of the adsorption configurations for hexene on Fe(110). The optimal geometry after the full optimization is shown on the right. In panel b, the corresponding adsorption are represented.